Before a variable name (identifier) can be used in a C program, it must be declared explicitly, together with its corresponding data type. There are some restrictions in giving a name to variables and constants. Names can be composed of letters and numbers, however the first character must be a letter. Capital (uppercase) letters and small (lowercase) letters are treated differently, so capital A is not the same with small a.
Keywords or commands such as case, int, float, if, do, for, etc., cannot be used as variable or constant names, because they are considered as reserved words. C programming language is a case-sensitive. This means that all keywords, commands and standard functions of C language must be written in lower case letters.
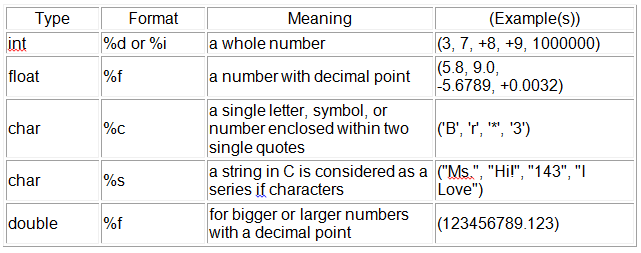
Basic Data Types of C
Control Characters
\a - alert (bell) character
\b - backspace
\n - new line/next line
\r - carriage return/Enter key
\t - horizontal tab
\v - vertical tab
\\ - backslash
\f - \form feed
‘ ‘ - single quote is used for single character / letter
" " - double quote is used for two or more character
{ - open curly brace signifies begin
} - close curly brace signifies end
& - address of operator
* - indirection operator / pointer